Your Western roman empire climate images are ready. Western roman empire climate are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Western roman empire climate files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for western roman empire climate images information related to the western roman empire climate keyword, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Western Roman Empire Climate. From AD 250 to 550 the climate flipped from one decade to the next between dry and cool and warm and wet. We can learn crucial lessons by examining the natural forces that shaped Romes rise and fall. According to multiple studies of paleoclimatic data-sets a climatic shift did indeed take place sometime after the Roman Optimum when a favourable climate was arguably decisive for the growth of the Roman Empire. This bibliometric analysis deals with research on the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire in connection with climate change.
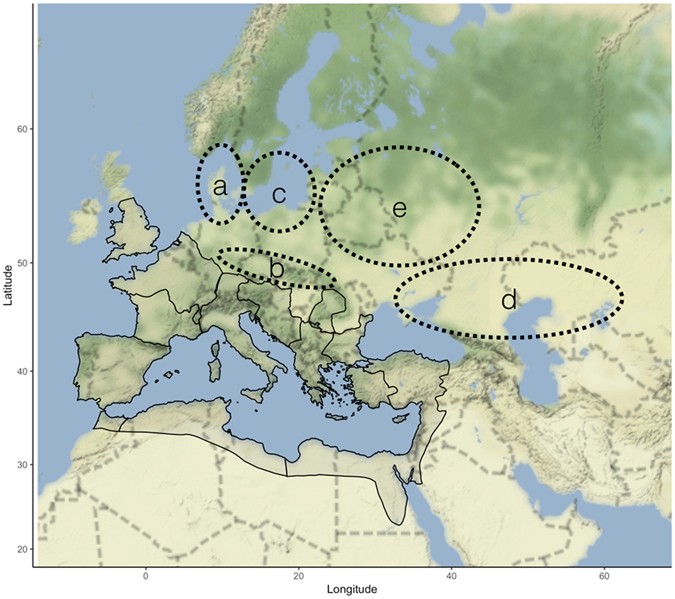 Changes In North Atlantic Oscillation Drove Population Migrations And The Collapse Of The Western Roman Empire Scientific Reports From nature.com
Changes In North Atlantic Oscillation Drove Population Migrations And The Collapse Of The Western Roman Empire Scientific Reports From nature.com
The kind of climate change thats supposed to have destroyed the Roman Empire is different than the current version. Climate crisis From the late summer of 1314 a hard rain began to fall across north-west Europe. The only debate is why the Empire could not. The lack of sunlight and drop in temperatures lead to mass crop failure. Historical circumstances may challenge recent political and fiscal reluctance to mitigate projected climate change. Climate Change - Total War.
Recently some scholars have argued that drought in Central Asia and the onset of a cooler climate in North-West Eurasia may have put Germanic tribes Goths and Huns on the move into the Roman Empire provoking the Migration Period and eventually leading to the downfall of the Western Roman Empire.
This blocked out sunlight causing an average drop in global temperatures of 2C the greatest in 2000 years. Wet and warm summers occurred during periods of Roman and medieval prosperity. The eruptions shot clouds of volcanic ash into the air. Based on the Web of Science WoS database we applied a combination of three different search queries for retrieving the relevant literature. Climate crisis From the late summer of 1314 a hard rain began to fall across north-west Europe. Attila Western Roman Empire LEGENDARY Difficulty Lets.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Sometime after AD 250400 however the climate turned unstable. Coincided with the demise of the western Roman Empire and the turmoil of the Migration Period. Climate Change - Total War. Lower temperatures negatively affected agriculture that caused famines and pestilences and that reduced the population. The kind of climate change thats supposed to have destroyed the Roman Empire is different than the current version.

The eruptions shot clouds of volcanic ash into the air. Shifts in the North Atlantic Oscillation NAO from 12 to 01 in four episodes increased droughts on the Roman Empires periphery and created push factors for migrations. The eruptions shot clouds of volcanic ash into the air. A combination of many. A combination of many factors interacting with each other is a possible explanation for the pattern of long-lasting decline and final collapse.

In the following years harvest after harvest failed. We can learn crucial lessons by examining the natural forces that shaped Romes rise and fall. This was caused by a solar maximum which had set in ca. The only debate is why the Empire could not. We are affected by global warming in ancient times the problem seems to have been global cooling.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
From AD 250 to 550 the climate flipped from one decade to the next between dry and cool and warm and wet. Increased climate variability from 250 to 600 CE. Increased climate variability from AD 250 to 600 coincided with the demise of the Western Roman Empire and the turmoil of the Migration Period. Climate flips and Black Death. The eruptions shot clouds of volcanic ash into the air.

The Western Roman Empire comprises the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court. Attila Western Roman Empire LEGENDARY Difficulty Lets. Climate changes tied to fall of Roman Empire A prolonged period of wet weather spurred the spread of the bubonic plague in medieval. Currently the number of records from different locations the toolbox of suitable analytic methods and the precision of dating are evolving rapidly contributing to an. Sometime after AD 250400 however the climate turned unstable.
 Source: wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
From AD 250 to 550 the climate flipped from one decade to the next between dry and cool and warm and wet. Climate Change - Total War. However climate is only one variable at play. Increased climate variability from AD 250 to 600 coincided with the demise of the Western Roman Empire and the turmoil of the Migration Period. The centuries during which the empire was built and flourished are known even to climate scientists as the Roman Climate Optimum From circa 200 BC to AD 150 it was warm wet and stable across.

Such historical data may provide a basis for counteracting the recent political and fiscal reluctance to mitigate projected climate change. A combination of many. The kind of climate change thats supposed to have destroyed the Roman Empire is different than the current version. In the following years harvest after harvest failed. How Climate Change and Plague Helped Bring Down the Roman Empire.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
What theories do you agree with most and least and why. Increased climate variability from AD 250 to 600 coincided with the demise of the Western Roman Empire and the turmoil of the Migration Period. The only debate is why the Empire could not. For months the weather was abysmal not only through the winter but into the next spring summer and beyond. 1 on the decline and fall of the Roman Empire in general 2 more specifically on the downfall in.
 Source: wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Such historical data may provide a basis for counteracting the recent political and fiscal reluctance to mitigate projected climate change. This bibliometric analysis deals with research on the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire in connection with climate change. Such decadal changes seem to have the most impact. We are affected by global warming in ancient times the problem seems to have been global cooling. Relatively modest changes in European climate in the past have had profound implications for society Penn State University climate scientist Michael.
 Source: workmall.com
Source: workmall.com
The kind of climate change thats supposed to have destroyed the Roman Empire is different than the current version. The objective of this lets play is to rebuild and reunite the Roman Empire so its influence covers the mapInitially this will be released on Monday Wednes. In particular this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 286 to 476 where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern. Shifts in the North Atlantic Oscillation NAO from 12 to 01 in four episodes increased droughts on the Roman Empires periphery and created push factors for migrations. However climate is only one variable at play.

In particular this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 286 to 476 where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern. From AD 250 to 550 the climate flipped from one decade to the next between dry and cool and warm and wet. Climate Change - Total War. A combination of many. This bibliometric analysis deals with research on the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire in connection with climate change.

The lack of sunlight and drop in temperatures lead to mass crop failure. Climate flips and Black Death. In particular this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 286 to 476 where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern. Further research suggested that this high-latitude eruption led to pronounced changes in hydroclimate including colder seasonal temperatures in specific Mediterranean regions during the two-year. However climate is only one variable at play.
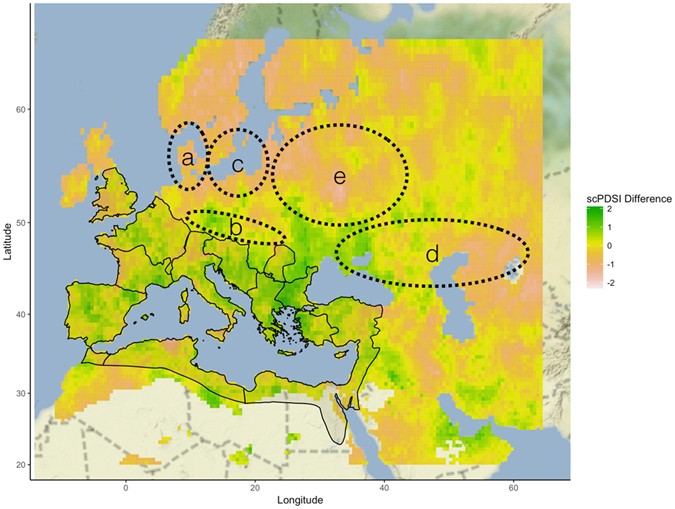 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Rivers burst their banks and fields flooded. The only debate is why the Empire could not. The kind of climate change thats supposed to have destroyed the Roman Empire is different than the current version. A combination of many. However climate is only one variable at play.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Currently the number of records from different locations the toolbox of suitable analytic methods and the precision of dating are evolving rapidly contributing to an. Rivers burst their banks and fields flooded. There is really no mystery per se as to why the Western Empire broke apart. Coincided with the demise of the western Roman Empire and the turmoil of the Migration Period. How Climate Change and Plague Helped Bring Down the Roman Empire.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
However climate is only one variable at play. There are 1001 reasons people give for the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. From climate change new religions moral decay immigration greedy soldiers and even lead poisoning. We are affected by global warming in ancient times the problem seems to have been global cooling. Lower temperatures negatively affected agriculture that caused famines and pestilences and that reduced the population.
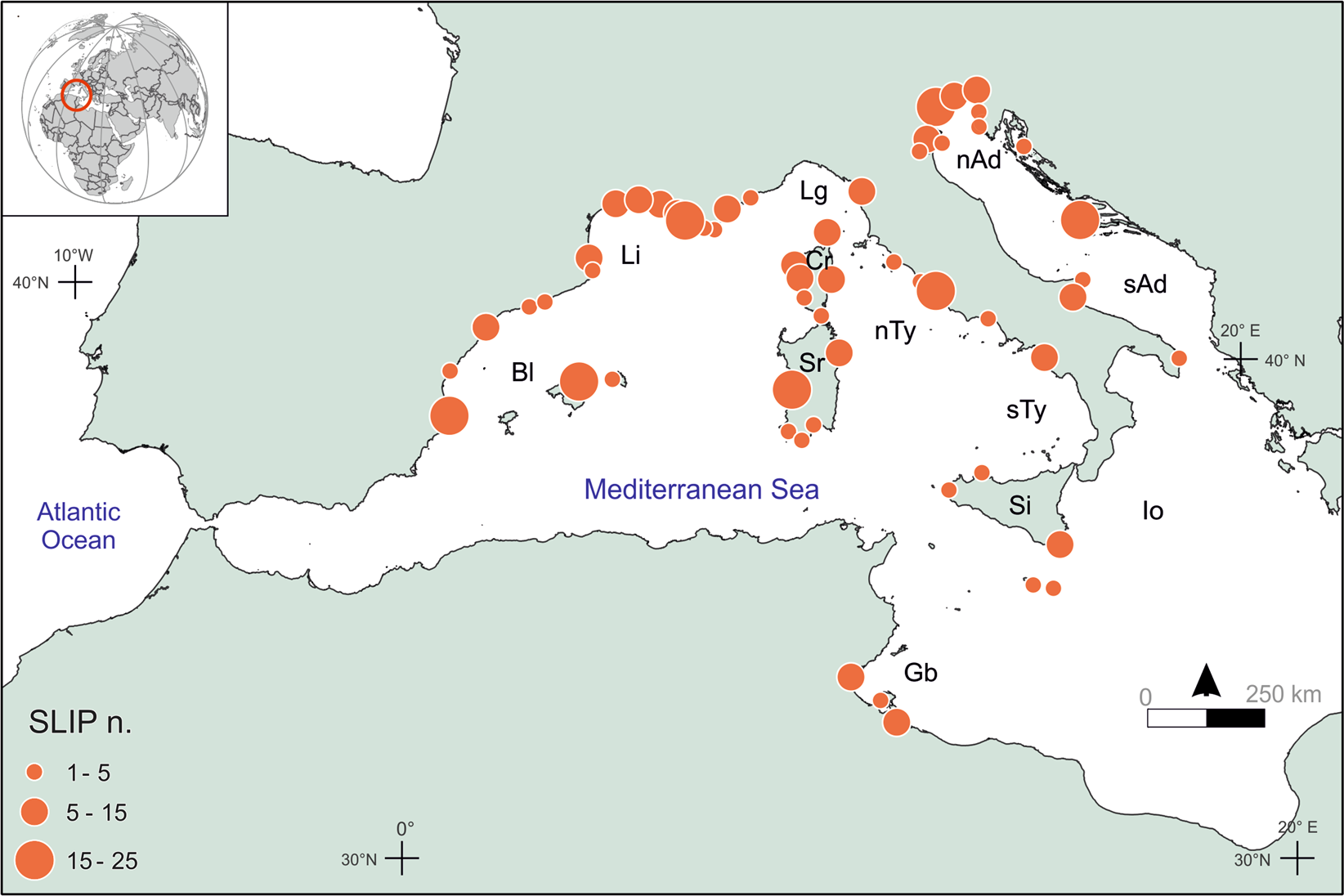 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Climate crisis From the late summer of 1314 a hard rain began to fall across north-west Europe. We can learn crucial lessons by examining the natural forces that shaped Romes rise and fall. Such decadal changes seem to have the most impact. What theories do you agree with most and least and why. The Roman Empire reached its maximum peak during a phase of warm wet and stable climate fostered by high stable solar activity and weak volcanic activity the Roman Climate Optimum or Roman Warm Period.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
We are affected by global warming in ancient times the problem seems to have been global cooling. This was caused by a solar maximum which had set in ca. This bibliometric analysis deals with research on the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire in connection with climate change. Currently the number of records from different locations the toolbox of suitable analytic methods and the precision of dating are evolving rapidly contributing to an. Climate flips and Black Death.
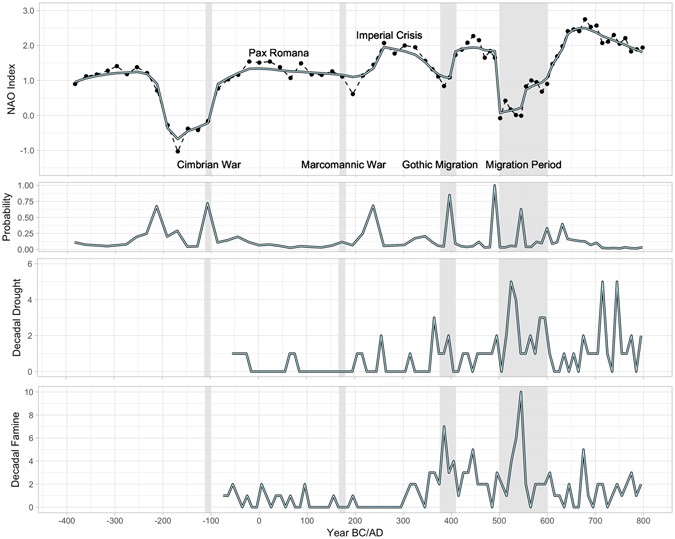 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
However climate is only one variable at play. Such decadal changes seem to have the most impact. We can learn crucial lessons by examining the natural forces that shaped Romes rise and fall. The objective of this lets play is to rebuild and reunite the Roman Empire so its influence covers the mapInitially this will be released on Monday Wednes. The lack of sunlight and drop in temperatures lead to mass crop failure.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title western roman empire climate by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






